- Mobile No: 8696907001 9433191919
- cvas910@gmail.com
Location & Climate
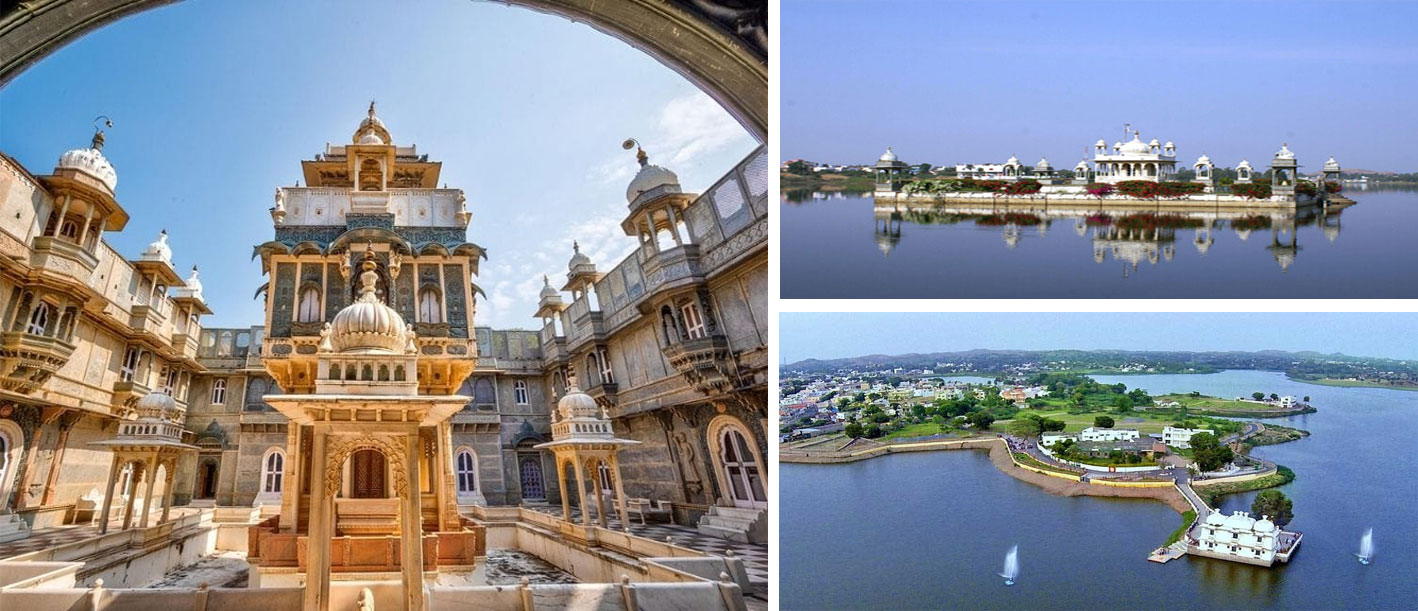
It is located in the southern part of Rajasthan between 23o20′ and 24o01′ north latitude and 73o21′ and 74o01′ east longitude. The town of Dungarpur itself is said to have been a Bhil ' Pal' or a hamlet of 'Dungaria', a Bhil Chieftain whom Rawal Veer Singh Dev caused to be assassinated in the fourteenth century
Dungarpur, town, southern Rajasthan state, northwestern India. It is situated on a level upland, about 50 miles (80 km) south of Udaipur.
Dungarpur was founded in the 14th century and was named for Dungaria, an independent chieftain of the Bhil people. It was the capital of the princely state of Dungarpur. The princely state was included in Banswara state until about 1530. Successively under Mughal, Maratha, and British control, it became part of the state of Rajasthan in 1948.
The town is an agricultural market centre and is linked by road with Udaipur as well as with Vadodara, Ahmadabad, and Indore via Godhra in Gujarat state. A hospital and a government college affiliated with the University of Rajasthan in Jaipur are located there. Dungarpur’s surrounding region consists of a hilly forested area drained by the Mahi River, which flows about 30 miles (48 km) east of the town. Agriculture is the principal occupation, and wheat, millet, rice, corn (maize), and pulses are the chief crops. Beryllium, lead, zinc, silver, iron ore, and mica deposits are worked extensively. Pop. (2001) 43,108; (2011) 47,706.


